Microwave Frequency Fiber Interferometry in Submarine Deployed Telecommunication Cables
A. Bogris et. al. | pre-print: https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05369 | Article pdf
-
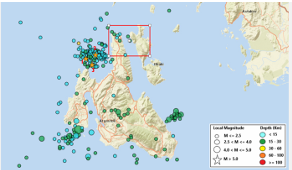
First-ever deployment of MFFI in a submarine environment, successfully operating over a 15.6 km telecom cable between Cephalonia and Ithaca, Greece.
-
Detected over 110 micro-earthquakes with magnitudes as low as 1.5, demonstrating sensitivity comparable to seismic stations and Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) systems.
-
Monitored tidal and ocean surface waves, showing clear correlations between strain data and environmental factors like wind speed and sea conditions.
-
Proved MFFI as a low-cost, robust alternative for high-sensitivity geophysical monitoring in underwater environments, using existing telecom infrastructure.
Sensing with submarine optical cables
A. Mecozzi | APL Photonics, Vol. 9, Issue 7, July 2024 | Article pdf
-
Introduced a theoretical framework for understanding how environmental disturbances (like earthquakes and ocean swells) can be detected using the state of polarization in megameter-long submarine optical cables.
-
Proposed a novel sensing scheme that enables the extraction of environmental perturbations at specific locations along the fiber, using the polarization of backreflected light—making localization of events possible.
-
Demonstrated the advantage of polarization sensing over phase-based methods for detecting very low-frequency signals, as it is less affected by laser phase noise.
-
Validated sensing potential with real-world examples, including earthquake and sea swell detection, using polarization data from a transoceanic fiber-optic link (the Curie cable between Los Angeles and Valparaíso).

